According to the European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association (ACEA), sales of hybrid-electric vehicles (HEVs) increased by 60.5 percent in 2021 compared to the previous year, overtaking diesel sales in the European Union for the first time. Meanwhile, plug-in hybrid-electric vehicles (PHEVs) experienced even more growth, as registrations increased 70.7 percent year-on-year during the same period.
Hyundai currently boasts the widest range of electrified powertrains on the market, including a number of HEV and PHEV eSUVs. In 2021, the company sold 515,886 units in Europe, a 21.6 percent increase compared to the previous year. Of these, 72,509 were zero-emission vehicles, which include battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) and fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) - accounting for 14.1 percent of sales in Europe.
Hyundai sold 109.84 percent more models in 2021, compared to 2020. The best-selling electrified Hyundai model in Europe was the Tucson Hybrid. Meanwhile, the company also saw a rise in PHEV sales - a 52.6 percent increase compared to the previous year.
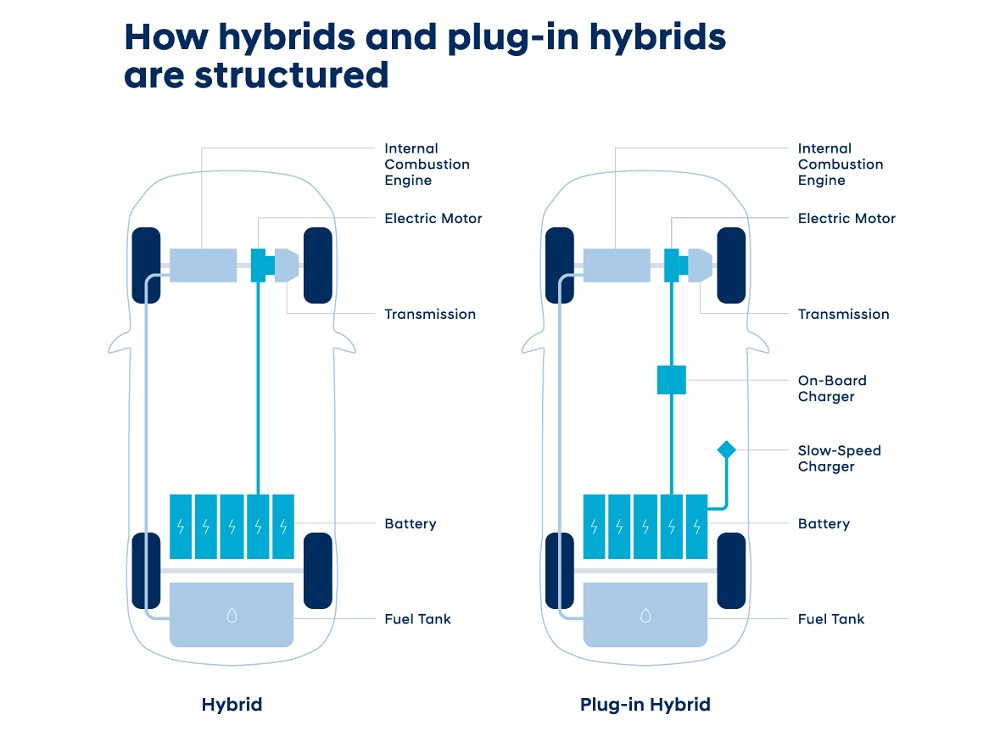
How HEVs and PHEVs work
The term ’hybrid’ signifies a vehicle that is outfitted with multiple combined power sources. An HEV features an ICE, an electric motor and a battery. HEVs are designed to sense exactly when the driver wants to accelerate. At lower speeds, only the electric motor is used. Accordingly, in scenarios where the driver accelerates harder or the vehicle requires more power, such as going up a hill, the ICE and the electric motor combine for the highest possible efficiency.
An HEV does not have to be plugged in to an external power source to recharge its battery. Instead, electric energy is generated through regenerative braking. It draws its power by converting any remaining kinetic energy left over while decelerating, braking or going downhill.
A PHEV, on the other hand, shares the
same basic design as an HEV, while also offering some of the benefits of
a BEV. Like an HEV, a plug-in hybrid-electric vehicle houses an ICE and
electric motor but is also equipped with a bigger battery for an
increased electrified range. In addition, these models are equipped with
onboard chargers for additional charging via an external power source.
A
PHEV can run purely on electric power, but will automatically switch
over to use the ICE, depending on the road or the driving conditions.
The ICE is a vital component because when the PHEV’s battery reaches a
pre-set state of charge, it enables the car to enter a charge sustaining
mode. When the battery is low, it will work in the same way as an HEV.
The ICE powers the wheels as normal, while regenerative braking will
supply power to recharge the electric battery. This extends the PHEV’s
overall range.
In traditional ICE cars, power generated from the
engine goes to the wheels through the transmission. Both HEVs and PHEVs
are equipped with an additional electric motor between the internal
combustion engine and the automatic transmission. The motor also
generates power, which supports the engine and improves acceleration and
fuel efficiency. Due to this, their power is generated from two sources
and delivered to the wheels through the transmission.
Hyundai’s
hybrid models do not feature a torque converter or a starting clutch,
and instead, utilise a six-speed automatic transmission (6AT). With 6AT,
drive off is managed with an electric motor.
In many HEV and
PHEVs, the high-voltage battery required for driving is separated from
the vehicle’s standard 12-volt lead-acid auxiliary battery. Hyundai’s
HEV models integrate the two batteries, and they are installed under the
second-row passenger seats. The 12-volt batteries of the PHEV models
are in the underbody of the boot. The benefits for the brand’s eSUV
customers are twofold. Firstly, this guarantees a greater volume of
space in the trunk. Secondly, it ensures the centre of gravity is closer
to the middle of the vehicle, which improves agility and driving
performance.
Hyundai’s HEV and PHEV models
For enhanced performance and reduced emissions, both the Tucson Hybrid and SantaFe Hybrid are assembled with a powerful 230 PS hybrid powertrain, which is a combination of Hyundai’s 1.6‑litre T-GDi ‘Smartstream’ engine and a 44.2 kW electric motor. The hybrid powertrain draws its power from the association of the T-GDi engine and a 1.49 kWh lithium-ion polymer battery. Both models are available with two- or four-wheel drive.
Meanwhile,
both the Tucson PHEV and SantaFe PHEV are also equipped with the
1.6‑litre T‑GDi ‘Smartstream’ engine. These models are paired with a
66.9 kW electric motor, which draws its power from a 13.8 kWh
lithium-ion polymer battery. The total power output of both models is
265 PS, with a combined torque of 350 Nm. Each model is equipped with a
four-wheel-drive as standard.
The Tucson Plug-in Hybrid emits
just 31 g/km of CO2 under WLTP driving conditions. Meanwhile, the
SantaFe Plug-in Hybrid emits 37 g/km of CO2 under WLTP conditions.
The
drivetrains of the HEV and PHEV variants of both models are available
with 6AT. Operated through shift by wire, meaning that the gear shift is
controlled with an electrical button instead of the classical lever,
6AT was optimised for an ideal balance of performance and fuel
efficiency.
Both the Tucson Plug-in Hybrid and SantaFe Plug-in
Hybrid are equipped with a 7.2 kW respectively 3.3 kW onboard charger,
for use at an EV charging station or via a home wall box. Bluelink users
can also check the battery charge level and manage the charging
settings of both models via the app.
Hyundai’s 1.6 T-GDI Smartstream engine features world-leading Continuously Variable Valve Duration technology
Optimising the engine performance and fuel efficiency of Hyundai’s HEV and PHEV models even more is the 1.6 T-GDI ‘Smartstream’ engine. This features Hyundai’s Continuously Variable Valve Duration (CVVD) technology, which was a world-first when it launched in 2019. The valve control technology regulates the duration the valve opens and closes, according to driving conditions.
When the vehicle is maintaining a constant speed and requires low engine output, CVVD holds the intake valve open until the middle of the compression stroke, and from that point closes it until near the end of the compression stroke. This helps to improve fuel efficiency by reducing the resistance caused by compression. Conversely, when engine output is high, for example when the car is driving at a high speed, the intake valve closes at the beginning of the compression stroke to maximise the amount of air used for the combustion. This enhances torque to improve acceleration.
CVVD is the only system that can change the duration of the valve opening whilst driving, depending on conditions. This technology increases performance by four per cent and fuel efficiency by five per cent while decreasing emissions by 12 percent.
To
further optimise fuel efficiency, the 1.6 T-GDI features Low-Pressure
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (LP EGR). The LP EGR returns some of the gas
burnt by the engine to the combustion chamber, producing a cooling
effect and reducing the emission of nitrogen oxides. The 1.6 T-GDI also
features a low-pressure system that redirects the burnt emission gas to
the front of the turbocharger compressor, rather than the intake system,
to increase efficiency under high load conditions.
For even more
assurance for its customers, Hyundai undertakes a vast number of safety
performance tests on its HEV and PHEV models’ lithium-ion polymer
batteries during development. The company is also focused on enhancing
battery safety and conducts extreme crash tests to test the three safety
features of the batteries: a ceramic coating separator, structures to
protect the battery from physical damage, and battery controllers.